SPD (Surge Protective Device) is a device that prevents electrical and electronic equipment from malfunctioning due to lightning. SPDs are installed in various places such as factories, buildings, and utility poles, and protect society in places that are not usually visible.
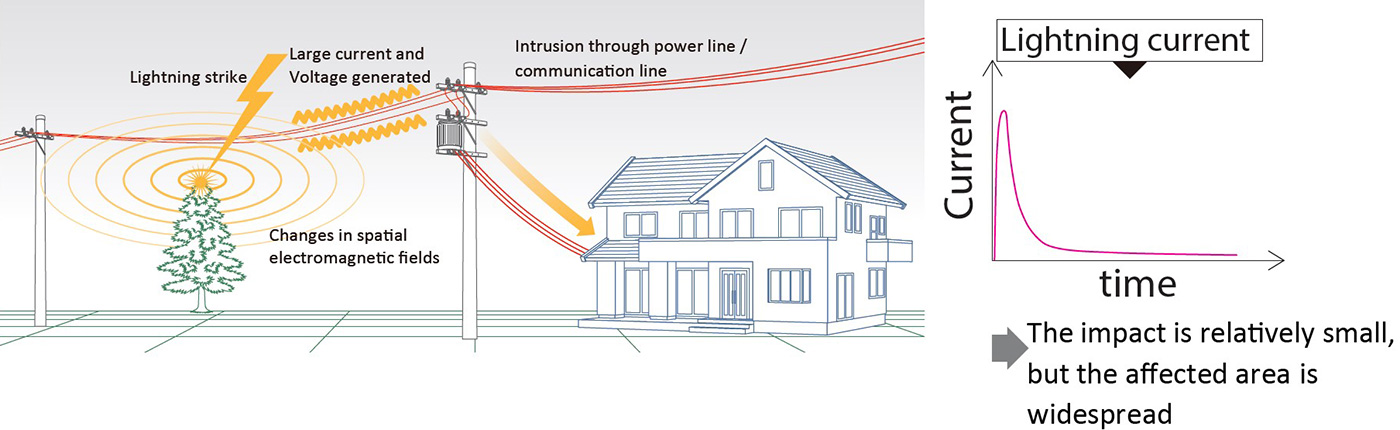
The current of lightning is very large and lightning strikes cause abnormal over-voltage and the over-current is generated temporarily in a short period of time called “lightning surge” in the vicinity.
The lightning surge enters the electrical equipment in the building through the power lines and communication lines and causes damage to the equipment.
The effects of this lightning surge can extend several kilometers away from the point where the lightning struck and can cause damage even if the lightning strike is not in the immediate vicinity.
。
It is a mistake to think that a lightning rod can protect equipment from lightning.
The role of lightning rods is to prevent buildings from being damaged by lightning and they cannot protect electronic devices inside buildings, such as machines in factories and telephones in offices.
SPDs (surge protective devices) are necessary to protect electrical and electronic equipment in buildings from lightning surges.
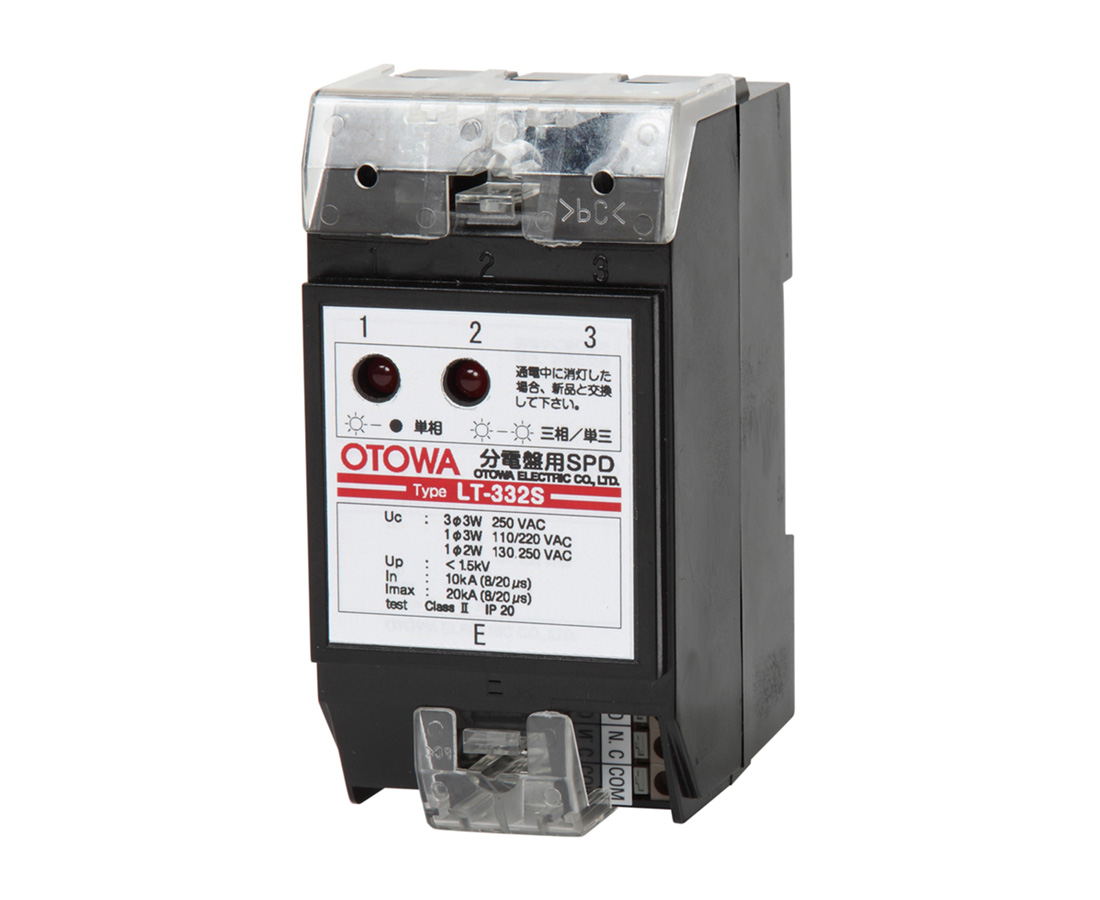

SPD for distribution boards
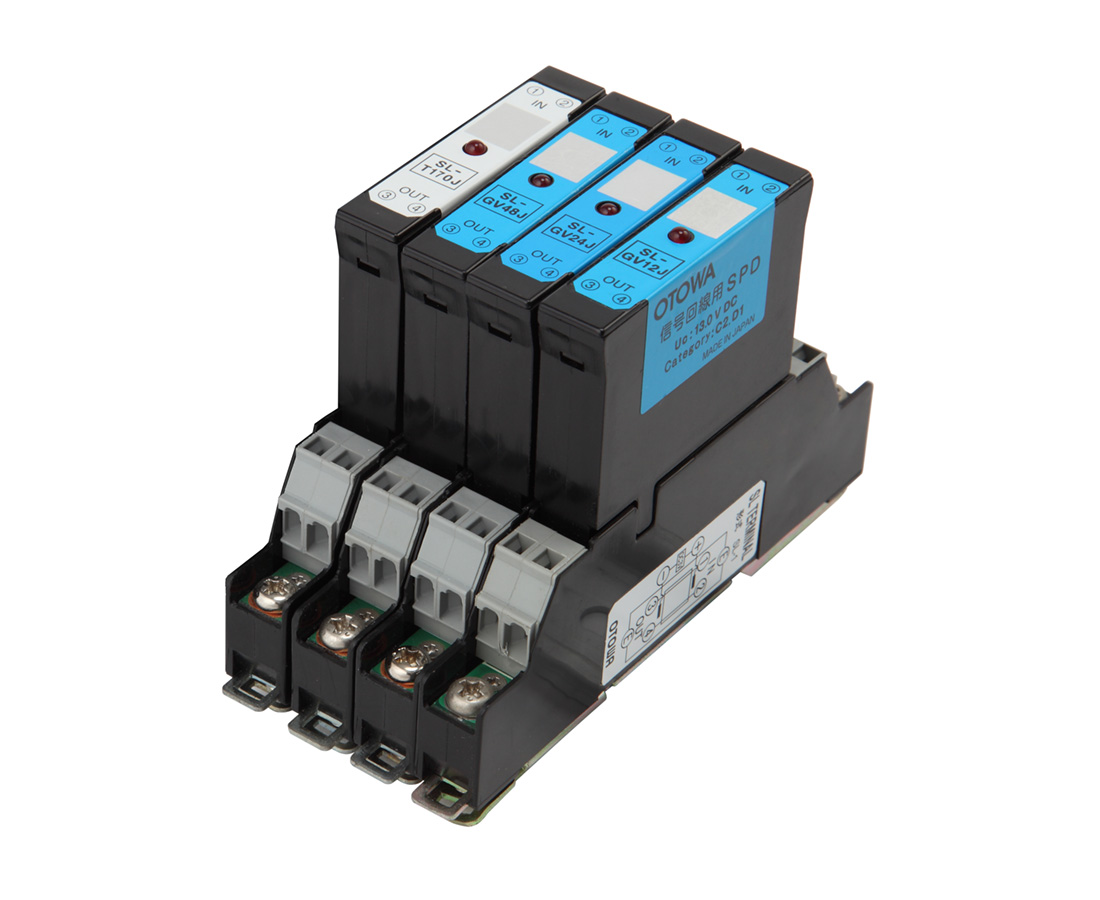

SPD for signal lines
The total amount of damage caused by lightning is said to be 100-200 billion* per year in Japan.
In recent years, electrical and electronic equipment has become increasingly micro computerized, highly integrated, ICT-oriented and is constantly exposed to the risk of lightning damage.
Damage can range from burning power cables (Photo 1) to damage to integrated circuits (Photo 2), which at first glance are difficult to identify as malfunctions.
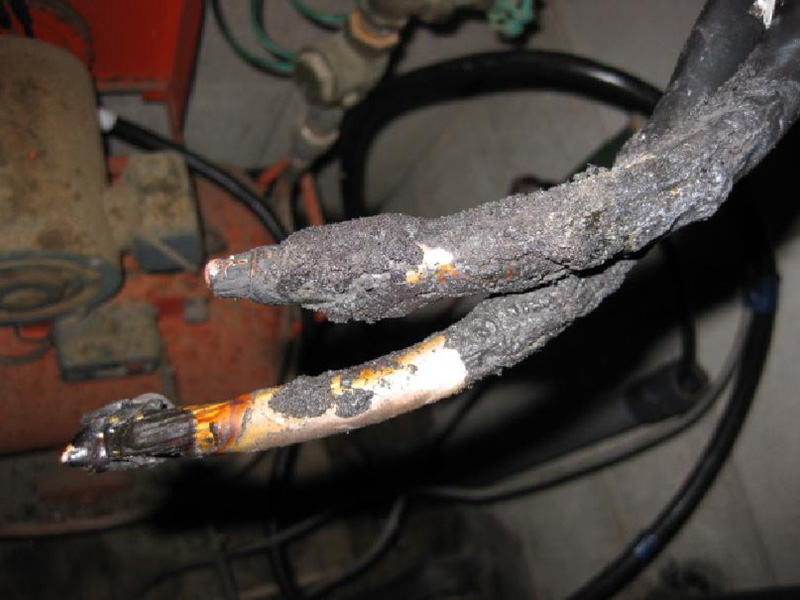

Photo 1
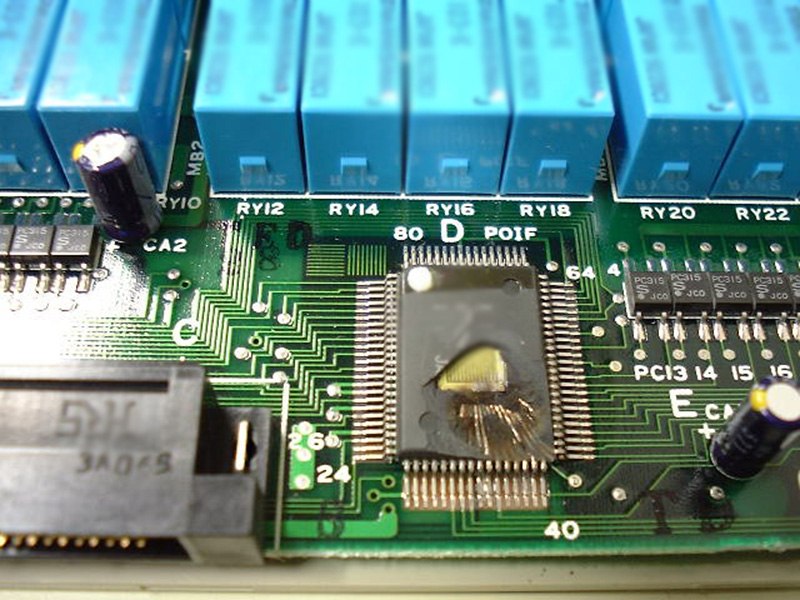

Photo 2
IEEJ, “IEEJ Technical Report No. 902” (2002)
The SPD contains at least one nonlinear component with the function of limiting transient overvoltages and diverting surge currents. Due to the characteristics of the nonlinear component, the SPD can protect equipment from surge events by limiting transient overvoltages. At normal operating supply voltages, the SPD is highly resistive and is equivalent to an insulator. However, when a transient overvoltages such as lightning surges occurs, the nonlinear component’s resistance decreases making it equivalent to a conductor which then diverts the surge current to ground. At this time, the SPD sends a lightning surge current to the ground and suppresses the lightning surge voltage. After it suppresses the lightning surge, it immediately returns to a high resistance state, in order to block follow current due to the supply voltage.
SPD: Surge Protective Device
SPD Aliases : Lightning arresters, arresters, surge protectors, etc.
※Nonlinear elements include MOV (metal oxide varistor), GDT(discharge tube with gas), ABD(avalanche break down diode), TSS (surge protection thyristor), etc.
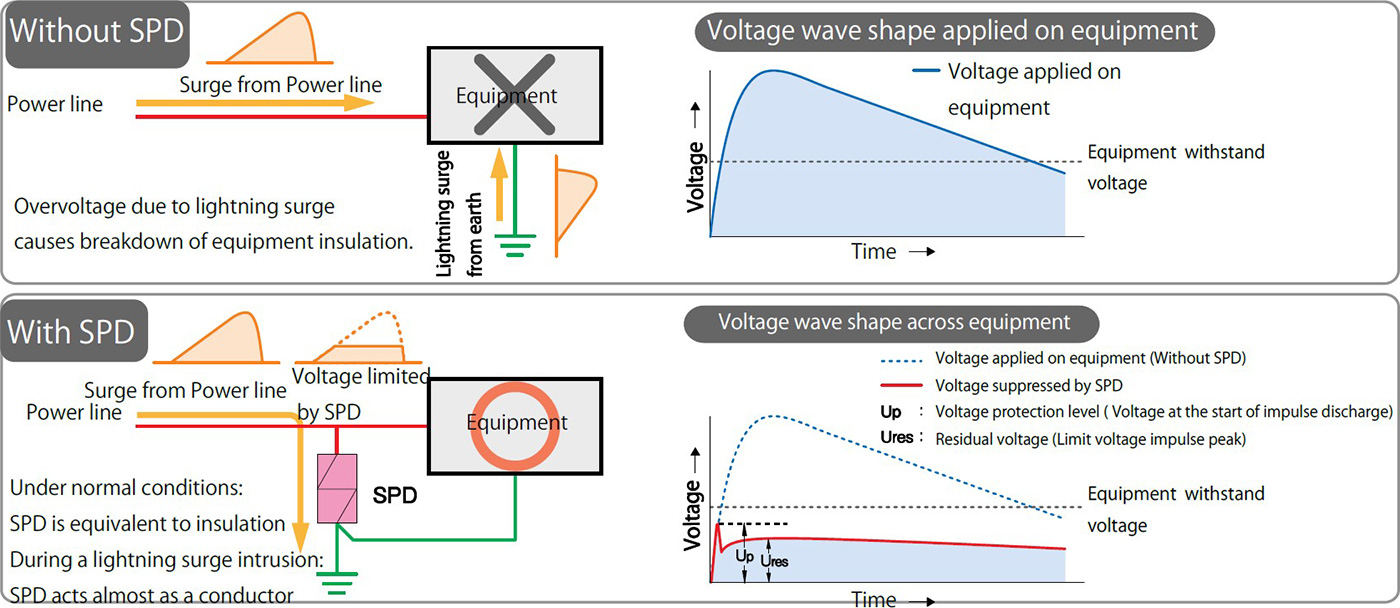
The SPD’s operating start voltage (V1mA) is slightly higher than the equipment’s operating voltage (AC100V in the case of the diagram on the right) and the SPD passes the surge portion that exceeds the operating start voltage to earth. At this time, residual voltage (voltage when lightning surge is handled, limiting voltage) is generated according to the size of the current.
The maximum discharge current of the SPD (wave height value of the current flowing through SPD, called Iimp for Class I and Imax for Class II in JIS) and the voltage protection level based on the residual voltage when SPD handles it normally are the key points for SPD selection.
The fundamental rule of LV SPD or even of high voltage arresters is to choose the arrester with the lowest possible voltage rating (to provide maximum margin of protection) which can survive the system’s generated temporary over-voltage conditions without failure.
This means that the users must check the information about their systems and the SPD products.
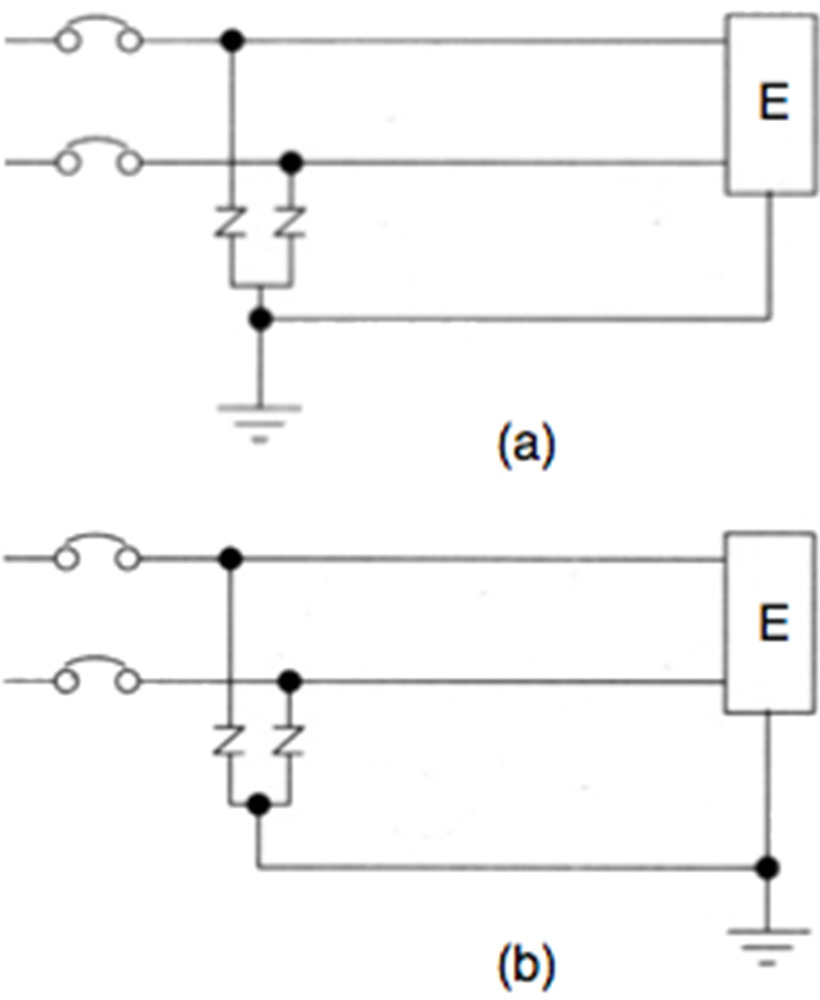
The way of ground connection differs effectiveness of protection greatly under the condition of surge invasion into the electrical system. The lightning current passing through the power line generates voltage by the voltage drop of the inductance of the line.
According to IEC standard, it is generally estimated that a 10kA surge current passing through 1m wire creates 1000V, and the voltage generation occurs along the surge path. Because of this phenomena the ground connection of below (a) can minimize the surge voltage applied to the equipment to be protected, where the connection (b) result in much more surge voltage to the equipment by the connection line from the SPD to the connection point to the ground.
The equipment protected by SPD is subject to a voltage equal to the sum of Up of SPD, Ub of circuit breaker and sum of inductive voltages of the lines along the surge path. Therefore, it is essential to minimize the length of connecting cables as short as possible: generally limited to 0.5m. V-connection of lead wire to the SPD as shown below (b) is an effective solution to reduce the wire length to minimum possible level.
In case the sum of wire lenth along the surge path exceeds 0.5m, additional measures need to be applied as below: